TNPSC Sub Inspector of fisheries Syllabus 2022:
Sub Inspector of fisheries Examination is conducted by Tamilnadu Public Service Commission(TNPSC). It’s not easy to clear the exam without knowing the TNPSC Sub Inspector of fisheries Examination syllabus 2022. First and foremost is to understand the revised syllabus, and go through it once before start preparing. The Sub Inspector of fisheries syllabus 2022 PDF is available in English and Tamil as a medium free download PDF. Check the syllabus, and go through each and every topic in the updated syllabus. Mark the important area/ topic to concentrate on in the upcoming exam. Prepare a detailed study plan and start preparing based on that study plan. TNPSC Sub Inspector of fisheries Syllabus 2022 in Tamil and English medium available in PDF below for free download.
For TNPSC Sub-Inspector of Fisheries Notification 2022, Check details – TNPSC Sub-Inspector of Fisheries Recruitment 2022
TNPSC Sub Inspector of fisheries Exam Pattern 2022:
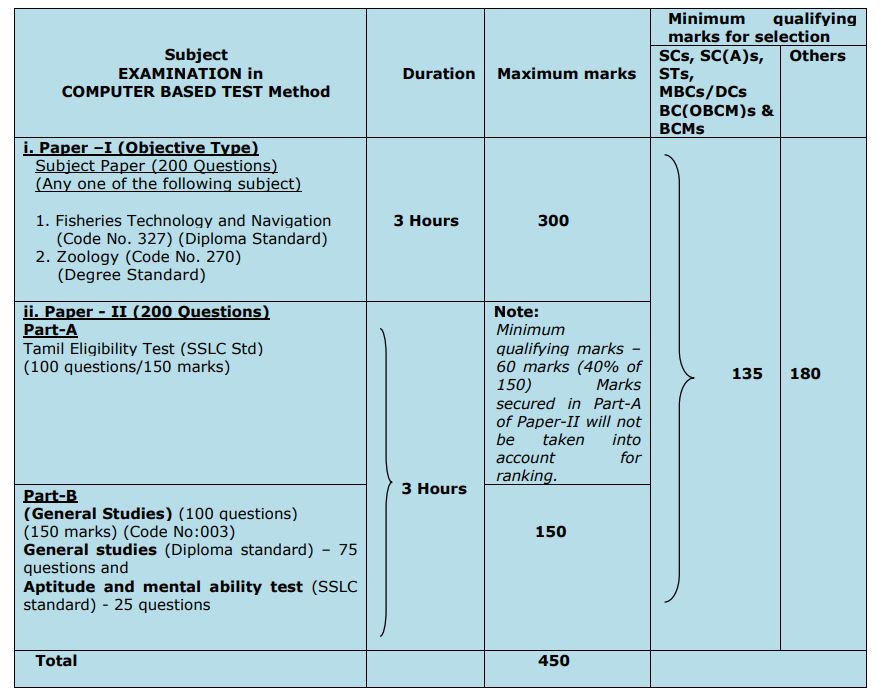
TNPSC Sub Inspector of Fisheries Syllabus 2022:
Paper-I
FISHERIES TECHNOLOGY AND NAVIGATION ENGINEERING
(DIPLOMA STANDARD)
UNIT –I: FISHERY BIOLOGY
Classification of fishes – Morphometric and Meristic Characters – Length weight Relationship- Food and Feeding Habits – Reproductive Biology- Fish Physiology – Developmental Biology of Fin Fish, Shell fishes – Aquatic Ecology.
UNIT –II: INLAND & MARINE FISHERIES
Capture fishery resources of India – Major Riverine fisheries of India – Lake Fisheries Reservoir Fisheries – Cold Water Fisheries – Pollution in Inland Waters. Principal Marine Fisheries of Indian Coasts–Crustaceanfishery resources-shrimps, lobsters- Molluscan resources-Gastropods, Bivalves- Seaweed Resources –– Von Betalanffy’s Growth equation –growth parameters – mortality parameters-Maximum Sustainable Yield-Distribution of living organisms in the Sea.
UNIT –III: NAUTICAL TECHNOLOGY
Compass – Navigational Charts – Mercator Projections – Buoyage System – International Codeflag signals –Navigational lights-Firefighting –Strom Signals – Distress Signals – Life Saving Appliances-Life buoy-Life jackets-Life raft.
UNIT – IV: FISH PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY
Proximate composition of fish –principle of fish spoilage– Rigor Mortis – Drying, Salt drying, Icing, Freezing, Canning, Fishery by products, Fish packaging technology.
UNIT –V: AQUACULTURE
Site selection for fish culture –composite fish culture– Plankton – Fertilization – Aqua feeds – Pond disinfection with lime -Water quality management – Disease control-common fresh water ornamental Fishes.
UNIT – VI: OCEANOGRAPHY AND METEOROLOGY
Waves- Tides- Currents- El – Nino – Salinity – Tsunamis – Weather – Climate – humidity- Tropical Cyclones – Atmospheric pressure.
UNIT –VII: FISHING GEAR AND CRAFT TECHNOLOGY
Classification of Fishing Gear – Fishing Gear Materials –Modern Fishing gears – Trawls, Gill, Nets, Longlines Fishing Gear Accessories – Fishing Crafts of Indian Coast – Wooden boat construction – Steel boat construction – FRP boat Construction-Dry docking.– Boat building yards.
UNIT –VIII: FISHERY ECONOMICS
Basic Economic terminologies – Elasticity – Price, Income – Cost, returns – Marketing – Co-operatives – Socio economic Survey – economics of fish and fish seed production system-economics of marine capture fisheries.
UNIT –IX: FISHERIES RESOURCE MANAGEMENT AND ADMINISTRATION
Open Access Fisheries- Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY),– Fishing holidays, Mesh size regulations- Growth over fishing – Recruitment over fishing – Ecosystem approach for fisheries management -EEZ-Marine fisheries regulations.
UNIT –X: FISHERY ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING
Site selection for fish farm- types of ponds-Pumps, Aerators, Sluice, Monk- canal types of dykes –Classification of Engines – Marine diesel Engines – parts of IC engines – Fishing machineries -Net hauler, Winch,.– Fish processing machineries.- Canning machineries-Refrigeration machineries. Principles of electricity-Batteries- Principles of Radio Transmission-RADAR –sound propagation in water – Fish finding Equipments – Echo Sounder – SONAR –– Communication Equipments – Radio Telephone.
ZOOLOGY
(DEGREE STANDARD)
UNIT I
Non-Chordata: General organisation – Classification with diagnostic features upto classes. Evalutionary relationship among taxa, symmetry.
Protozoa: Structure, reproduction and life history of Amoeba, Paramecium, Trypanosoma, Plasmodium, Monocystis, Leishmania – locomotion, nutrition, economic importance. Porifera: Sponges canal system, skeleton, reproduction and economic importance.
Coelenterata: Diploblastic organization – life history of obelia and Aurelia, Metagenesis – Polymorphism in Hydrozoa. Corals and Coral formation – relationships of Cnidaria and Acnidaria. Helminthes: Structure and life history of Planaria, Fasciola, Teania, Ascaris and Wucheriria – parasitic adaptations – Helminthes in relation to man.
Annelida: Nereis, earthworm and leech – Coelom and metamerism – modes of life in polychactes. Onychophora: Structure, affinities and distribution of Peripatus.
Arthropoda: Prawn, Scorpion and Cockroach – Larval forms and parasitism in Crustacea – Mouth parts, vision, respiration and excretion. Metamorphosis and social life in insects. Mollusca: Freshwater mussel, pila, sepia.
Echinodermata: General organisation – Watervascular system. Larval forms and affinities.
UNIT II
Prochordata: Amphioxus, Balanoglossus – Ascidian retrogressive Metamorphosis, neoteny and affinities.
Chordata: General Organisation – Characters, Outline, classification upto class level.
Pisces: Locomotion, migration, respiration, Parental care, economic importance; structure and affinities of dipnoi.
Amphibia: Origin of amphibians – Respiration, Parental care – South Indian amphibians.
Reptiles: Origin – Conquest of land – adaptations to live on land, adaptive radiation – Temporal Vacuities – identification of poisonous and nonpoisonous snakes – poisonapparatus – South Indian snakes.
Birds: Origin – flight adaptations – mechanism of flight – double respiration – migration -Flightless birds
Mammals: Dentition, skin derivatives – distribution – adaptive radiation. Protothria, Metatheria, eutheria and their Phylogenetic relationships.
UNIT III
Cell and Molecular Biology: Cellular Organelles – Structure and function – Plasma membrane, Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Endoplasmic reticulum and Ribosomes – Nucleus and Nucleolus. Cell division, cell cycle; Chromosomes – DNA structure and function, replication of DNA, Genetic code – RNA and protein synthesis. Geneexpression, regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Recombinant DNA – Genetic engineering, its uses in agriculture, industries and medicine.
UNIT IV
Genetics: Mendelian concepts, multiple alleles, blood groups, Rh-factor. Linkage, crossing over – mutation (Natural and induced); Sex chromosomes, Sex determination and Sex Linked inheritance – Chromosome number and form ploidy – cytoplasmic inheritance – Karyo types – chromosome mapping, Normal and abnormal genetic disorders; Bio-chemical genetics – Eugenics. Human genome Project.
Biostatistics: Mean, Median and standard deviation. Bio-informatics: DNA and Protein sequence analysis, Prediction functional structure, protein folding, Phylogenetic tree construction.
UNIT V
Bio Chemistry: Bio-molecules, Structure and role of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and amino acids – Glycolysis and kreb’s cycle – oxidation, reduction – oxidative phosphorylation – energy conservation and release, cyclic AMP, ATP; enzymes – mechanism; Hormones-classification biosynthesis and function.
Physiology: With reference to mammals, digestion, nutrition, balanced diet – assimilation, intermediary/metabolism. Composition of blood – Coagulation, Transport of oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Blood pigments, Mechanism of respiration. Muscles, mechanism of muscle contraction. Temperature regulation, Acid base balance and homeostasis, Nerve impulses and conduction, neurotransmitters. Receptors- photo, phono and chemo reception. Nephron and urine formation. Endocrine glands, testis, ovary and pituitary organs and their inter relationship.
Physiology ofreproduction in humans, Hormonal development in insects, pheromones and their uses. Bioluminescence. Biological clock. Physiology of immune response- Antigens – Immuno globulins – humoral and cell mediated immunity. T and B cells,
mechanism of antibody formation – Immunodeficiency diseases; vaccination.
UNIT VI
Development Biology: Gametogenesis – fertilization, Pathenogenesis, type of eggs – blastulation, cleavage and gastrulation in frog and chick. Morphogenetic movements – organizer, potency, organogenesis with reference to ear, eye, kidney, brain. Formation and fate of extra embryonic membranes in chick. Plancentation- types, functions. – metamorphosis in Frog – Regeneration. Stem cellssources, types and their uses in human welfare, IVF, embryo transfer and cloning – Agingand senescence.
UNIT VII
Environmental Biology: Biotic and abiotic factors, their role, Intra and inter specific association. Biogeochemical cycles. Ecosystem- structure and function of ecosystems, types of ecosystems. Ecological succession, Community structure – Stratification. Population and Population dynamic – Habitat ecology. Wild life, need for conservation management and methods of conservation. Sanctuaries with special reference to Tamil Nadu. Pollution – air, water and land – Perspective policy planning for the environment.
UNIT VIII
Evolution: Origin of life – Evolutionary theories – Contributions of Lamarck, Darwin and De Vries – present status of Darwinism and Lamarkism – modern synthetic concept – Hardy Weinberg Law – Polymorphism and mimicry in evolution. Speciation: evolutionary species concept – Isolation, mechanisms and their role, role of hybridization in evolution. Fossils and Fossilization, Indian fossils, Geological time scale. Origin and evolution of horse and man – Culture evolution and Biochemical evolution.
Animal distribution: Zoogeographical distribution – Continental and island fauna – Continental drift – Discontinuous distribution, adaptive radiation. Natural resources and their conservation. Alternative sources of energy.
UNIT IX
Economic Zoology: Parasitism and Commensalism – Protozoan Parasites and diseases, helminthes parasites and diseases of man and domestic animals; Beneficial and harmful insects. Insect pests on crops and stored products – Control methods. IPM. Sericulture, apiculture, lac culture, seaweed culture, vermiculture, – oyster culture and pearl formation, poultry, pisciculture and induced breeding, Shell fisheries, Aquaculture practices in Tamil Nadu and their impact on the environment and on agriculture.
UNIT X
Instrumentation and Bio-techniques: Microscopy-Phase contrast, fluorescent, TEM, SEM.Colorimetric techniques, Centrifugation techniques. Fixation, staining techniques.
Electrophoretic techniques: Principles, AGE and PAGE. DNA finger printing, RFLP, RAPD and AFLP.
PAPER – II SYLLABUS FOR WRITTEN EXAMINATION
Part-A கட்டாய தமிழ்மொழி தகுதித் தேர்விற்கான பாடத்திட்டம் (கொள்குறி வினாவிற்கான தலைப்புகள்) பத்தாம் வகுப்பு தரம்
1. பிரித்தெழுதுதல் / சேர்த்தெழுதுதல்.
- எதிர்ச்சொல்லை எடுத்தெழுதுதல்.
- பொருந்தாச் சொல்லைக்கண்டறிதல்.
- பிழைதிருத்தம் (i) சந்திப்பிழையை நீக்குதல் (ii)மரபுப்பிழைகள், வழுவுச் சொற்களை நீக்குதல் / பிறமொழிச்சொற்களை நீக்குதல்.
- ஆங்கிலச் சொல்லுக்கு நேரான தமிழ்ச்சொல்லை அறிதல்.
- ஒலி மற்றும் பொருள் வேறுபாடறிந்து சரியான பொருளையறிதல்.
- ஒரு பொருள் தரும் பல சொற்கள்.
- வேர்ச்சொல்லைத் தேர்வு செய்தல்.
- வேர்ச்சொல்லைக் கொடுத்து / வினைமுற்று, வினையெச்சம், வினையாலணையும் பெயர், தொழிற்பெயரை / உருவாக்கல். 10. அகரவரிசைப்படி சொற்களை சீர் செய்தல்.
- சொற்களை ஒழுங்குப்படுத்தி சொற்றொடராக்குதல்.
- இருவினைகளின் பொருள் வேறுபாடு அறிதல். (எ.கா.) குவிந்து-குவித்து
- விடைக்கேற்ற வினாவைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்தல்.
- எவ்வகை வாக்கியம் எனக் கண்டெழுதுதல் – தன்வினை, பிறவினை, செய்வினை, செயப்பாட்டு வினை வாக்கியங்களைக்கண்டெழுதுதல்.
- உவமையால் விளக்கப்பெறும் பொருத்தமான பொருளைத் தேர்ந்தெழுதுதல்
- அனுவல் சார்ந்த சொற்கள் (கலைச்சொல்)
- விடைவகைகள்.
- பிறமொழிச் சொற்களுக்கு இணையான தமிழ்ச் சொற்களைக் கண்டறிதல் (எ.கா.) கோல்டு பிஸ்கட் – தங்கக்கட்டி.
- ஊர்ப்பெயர்களின் மரூஉவை எழுதுக (எ.கா.) தஞ்சாவூர் – தஞ்சை
- நிறுத்தற்குறிகளை அறிதல்.
- பேச்சுவழக்கு, எழுத்துவழக்கு (வாரான் – வருகிறான்).
- சொற்களை இணைத்து புதிய சொல் உருவாக்கல்.
- பொருத்தமான காலம் அமைத்தல்
(இறந்தகாலம், நிகழ்காலம், எதிர்காலம்). - சரியான வினாச்சொல்லைத் தேர்ந்தெடு.
- சரியான இணைப்புச் சொல்
(எனவே, ஏனெனில், ஆகையால், அதனால், அதுபோல). - அடைப்புக்குள் உள்ள சொல்லைத் தகுந்த இடத்தில் சேர்க்க. 27. இருபொருள் தருக.
28. குறில் – நெடில் மாற்றம், பொருள் வேறுபாடு. - கூற்று, காரணம் – சரியா? தவறா?
- கலைச்சொற்களை அறிதல்
எ.கா. – Artificial Intelligence – செயற்கைநுண்ணறிவு
Super Computer – மீத்திறன் கணினி
- பொருத்தமான பொருளைத் தெரிவு செய்தல்
- சொற்களின் கூட்டுப் பெயர்கள் (எ.கா.) புல் -புற்கள்
- சரியான தொடரைத் தேர்ந்தெடுத்தல்
- பிழைதிருத்துதல் (ஒரு-ஓர்)
- சொல் – பொருள் – பொருத்துக – கெர்
- ஒருமை பன்மையிழை
- பத்தியிலிருந்து வினாவிற்கான சரியான விடையைத் தேர்ந்தெடு.
Paper-II
Part-B
General Studies (Diploma Standard)
(Topics for Objective Type)
1. GENERAL SCIENCE
i. Nature of Universe – Measurement of Physical Quantities – General Scientific Laws in Motion –Force, Pressure and Energy – Everyday
application of the basic principles of Mechanics, Electricity, Magnetism, Light, Sound, Heat and Nuclear Physics in our daily life.
ii. Elements and Compounds, Acids, Bases, Salts, Petroleum Products, Fertilizers, Pesticides, Metallurgy and Food Adulterants.
iii. Main concepts of Life Science, Classification of living organisms, Evolution, Genetics, Physiology, Nutrition, Health and Hygiene, Human diseases.
iv. Environmental Science.
2. CURRENT EVENTS
i. Latest diary of events – National symbols–Profile of states –Eminent personalities and places in news–Sports –Books and Authors.
ii. Welfare Scheme of Government – Political parties and Political system in Tamil Nadu and India.
iii. Latest inventions in Science and Technology – Geographical Land Marks – Current Socio – Economic issues.
3. GEOGRAPHY
i. Earth Location – Physical Features – Monsoon, rainfall, weather and climate– Water resources–Rivers –Soil, Minerals and Natural resources– Forest and Wildlife–Agriculture pattern.
ii. Transport– Communication.
iii. Population density and distribution in Tamil Nadu and India.
iv. Calamities–Disaster Management–Environment – Climate change.
4. HISTORY AND CULTURE OF INDIA
i. Indus Valley Civilization –Guptas, Delhi Sultans, Mughals and Marathas – South Indian History.
ii. Characteristics of Indian Culture, Unity in Diversity–Race, Language, Custom.
iii. India as a Secular State.
5. INDIAN POLITY
i. Constitution of India–Preamble to the Constitution–Salient features of the Constitution–Union, State and Union Territory.
ii. Citizenship, Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy.
iii. Union Executive, Union Legislature–State Executive, State Legislature– Local Governments, Panchayat Raj.
iv. Spirit of Federalism: Centre-State Relationships.
v. Election–Judiciary in India–Rule of Law.
vi. Corruption in public life – Anti-Corruption measures – Lokpal and Lokayukta – Right to Information – Empowerment of Women – Consumer Protection Forums – Human Rights Charter.
6. INDIAN ECONOMY
i. Nature of Indian economy–Five year plan models – an assessment – Planning Commission and NITI Aayog.
ii. Sources of revenue–Reserve Bank of India – Finance Commission– Resource sharing between Union and State Governments –Goods and
Services Tax.
iii. Economic Trends – Employment Generation, Land Reforms and Agriculture – Application of Science and Technology in Agriculture – Industrial growth – Rural Welfare oriented programmes – Social Problems –Population, Education, Health, Employment, Poverty.
7. INDIAN NATIONAL MOVEMENT
i. National Renaissance –Early uprising against British Rule–Indian National Congress – Emergence of Leaders –B.R.Ambedkar, Bhagat Singh, Bharathiar, V.O.Chidambaranar, Thanthai Periyar, Jawaharlal Nehru, Rabindranath Tagore, Kamarajar, Mahatma Gandhi, Maulana AbulKalam Azad, Rajaji, Subhash Chandra Bose, Muthulaksmi Ammaiyar, Muvalur Ramamirtham and other National Leaders.
ii. Different modes of Agitation of Tamil Nadu and movements
8. HISTORY, CULTURE,HERITAGEANDSOCIO-POLITICAL MOVEMENTS OF TAMIL NADU
i. History of Tamil Society, related Archaeological Discoveries, Tamil Literature from Sangam age till contemporary times.
ii. Thirukkural:
a) Significance as a Secular Literature.
b) Relevance to Everyday Life.
c) Impact of Thirukkural on Humanity.
d) Thirukkural and Universal Values – Equality, Humanism etc.
e) Relevance to Socio – Politico –Economic affairs.
f) Philosophical content in Thirukkural.
iii. Role of Tamil Nadu in freedom struggle – Early agitations against British
Rule – Role of women in freedom struggle.
iv.iv. Various Social reformers, Social reform movements and
Social transformation of Tamil Nadu.
9. DEVELOPMENT ADMINISTRATION IN TAMIL NADU
i. Social Justice and Social Harmony as the Cornerstones of Socio-Economic Development.
ii. Education and Health systems in Tamil Nadu.
iii. Geography of Tamil Nadu and its impact on Economic growth.
10. APTITUDE & MENTAL ABILITY TESTS
i. Simplification–Percentage–Highest Common Factor (HCF)– Lowest Common Multiple(LCM).
ii. Ratio and Proportion.
iii. Simple Interest– Compound Interest–Area–Volume–Time and Work.
iv. Logical Reasoning – Puzzles – Dice–Visual Reasoning–Alpha Numeric Reasoning– Number Series.
Click here to download the Sub Inspector of fisheries Syllabus PDF 2022 – Download
