TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer Chemistry Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2023:
Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) has given an employment notification for the recruitment of 31 Junior Scientific Officers in the Tamil Nadu Forensic Sciences Subordinate Service. Candidates with an M.Sc. Degree in a relevant stream looking for TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer check the Official notification @ www.tnpsc.gov.in or you can see it below. Eligible candidates can apply online directly and also see the TNPSC JSO Exam Pattern, Syllabus, Education Qualification, Selection Process, and Important details below. Check the complete TNPSC JSO Chemistry Syllabus available both in Tamil & English before preparing for Written Examination(CBT). See TNPSC JSO Chemistry Syllabus 2023 and Exam Pattern below:
TNPSC JSO Paper I Syllabus for Chemistry – questions based on PG Degree Standard. TNPSC JSO Paper II Syllabus is based on Tamil Eligibility Test & General Studies. Check the complete JSO Chemistry Syllabus below both in text and in PDF format. Interested candidates check the complete syllabus and exam pattern of JSO below and also download the same. See the TNPSC JSO Chemistry Exam Pattern and Syllabus PDF Tamil and English below:
To see the complete Notification of TNPSC JSO Recruitment, check the link – TNPSC JSO Recruitment 2023
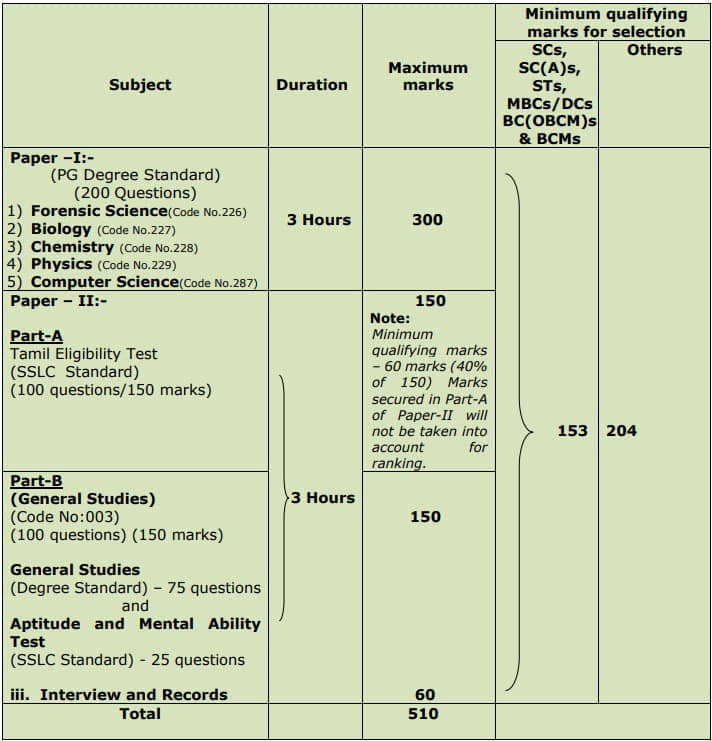
TNPSC JSO Chemistry Exam Pattern:
TNPSC JSO Chemistry Selection is based on a Written Examination (Objective Type) (Computer Based Examination)
– Written Examination is of Paper-I: Chemistry (PG Degree Standard) and Paper-II: Part A (Tamil Eligibility Test) & Part B (General Studies)
Junior Scientific Officer Paper I Chemistry Syllabus PDF:
The complete syllabus for JSO in Tamil and English is given below. See the full TNPSC JSO Paper I Syllabus below:
Paper I – Syllabus: Chemistry (PG Degree Standard)
Unit – I: Quantum Chemistry: Quantum mechanical postulates – Eigenvalue and function – the Schrodinger wave equation – elementary applications of Schrodinger’s equation – the particle in a box (one, two, and three-dimensional cases) – particle in a ring. The harmonic oscillator –the rigid rotor – the hydrogen atom – the Schrodinger equation for hydrogen atom – angular momentum – term symbols – Approximation methods – perturbation and variation method – application to hydrogen and helium atoms – R.S. coupling and term symbols for atoms in the ground state – Slaterorbital and HF – SCF methods Born open – Heimer approximation – valence bond theory for hydrogen molecule – LACO – MO theory for di and polyatomic molecules – concept of hybridization – Huckel theory for conjugated molecules (ethylene butadiene and benzene) – semi-empirical methods.
Unit – II: Chemical Kinetics and Thermodynamics: Rate laws – rate constant for first, second, third, and zero-order reaction – Half-life period Temperature dependence on rate – Arrenhenius theory – collision theory – Absolute reaction rate theory – ionic reaction – salt effect catalysis – Laws of photochemistry, quantum efficiency – photophysical processes of electronic excited molecules.
Partial molar properties – Chemical Potential – Partial molar volume and molar heat content – significance and determination Thermodynamics of real gases – gas mixture – fugacity definition – determination of fugacity variation of fugacity with temperature and pressure – the concept of thermodynamic probability – distribution of distinguishable and non – distinguishable particles. Maxwell – Boltzmann, Fermi-Dirac, and Bose-Einstein statistics – modes of contribution to energy – partition function – translational, vibrational, and rotational partition functions for mono, diatomic, and polyatomic ideal gases.
Unit – III: Nuclear Chemistry: Nuclear properties –nuclear spin and moments, origin of nuclear forces, salient features of liquid drop and shell models. Types of radioactive decay: Orbital electron capture, nuclear isomerism, internal conversion, detection and determination of activity by cloud chamber, nuclear emulsion, bubble chamber, G.M., Scintillation and Cherenkov counters; Accelerators – Linear and Cyclotron. Nuclear reaction: Types, reaction cross section, Q-value, threshold energy, compound nucleus theory: nuclear fission and fusion reactions as energy
sources: photonuclear and thermonuclear reactions. Components of nuclear reactor – the fast breeder reactor – nuclear reactors in India. Radioactive tracer – principles of tracer technique – application of tracers in the study of reaction mechanism and in analytical chemistry – neutron activation analysis, isotope dilution analysis – radio chemical determination of the age of the geological specimen. Tracers as applied to industry and agriculture – radioactive tracer in the diagnosis and treatment in the field of medicine.
Unit- IV: Electrochemistry: Mean ionic activity and activity coefficient: concept of ionic strength, Debye-Huckel theory of strong electrolytes – activity coefficient of strong electrolytes-determination – Deby Huckel limiting law at an appreciable concentration of electrolytes – Debye Huckel Bronsted equation – qualitative and quantitative verification. PH & PKa of acids and bases – determents and buffer actions conductometric and potentiometric titrations Mechanism of electrode reaction – polarization and overpotential. Corrosion and passivation of metals: Pourbaix and Evans diagrams –fuel cells – electrodeposition – principle, applications and anti-corrosion techniques.
Unit – V: Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiations and quantization of energy: Rotational spectra of diatomic molecules – isotopic substitution and rotational constants – vibrations spectra of linear symmetric, linear asymmetric and bent tri atomic molecules – electronic spectra – selection rules – nuclear magnetic resonance – chemical shifts – spin–spin coupling – electron spin resonance and hyperfine splitting theoretical principles of mass spectroscopy.
Application of UV, IR, NMR, ESR, and mass spectroscopy for structural elucidation of organic compounds, inorganic complexes, and free radicals.
Unit – VI: Organometallic compounds, Bioinorganic chemistry, and Polymers: Metal carbonyls, Metal nitrosyls, metal alkyl, alkenes and arene compounds – organic metallic compounds in catalysis – Chemistry of porphyrins – chlorophyll hemoglobin, myoglobin, ferredoxin, rubredoxin and cytochromes. Preparation and uses of polyethylene and uses of polyethylene, poly butylenes PVC, Nylon – Ziegler – Natta catalysts – Inorganic Polymers such as silicones, Borazines and phosphonitrilic compounds.
Unit – VII: Organic reaction mechanism and Stereochemistry: General methods of reaction mechanisms (Kinetic and non-kinetic) SN 1, S N 2 mechanisms – addition substitution, elimination and rearrangements – free radical mechanism – aromatic substitution – formation and stability of reactive intermediates – The arenium ion mechanism. Orientation and reactivity (ortho, meta and para directing groups). Typical reactions to be studied – nitration, halogenations, alkylation, acylation and diazonium coupling. Formylation – Gatterman, Gatterman-Koch, Vilsmeyer- Hack & Reimer-Tieman, Ziegler alkylation, Chichibabin, Aldol condensation – Claisen condensation – Perkin, Cannizaro, Fridel Craft, Favorski, Strok enamine – Michael addition – Baeyer – villager – Chichibabin. Pericyclic reactions – classification and examples Woodward and Hoffmann rules – use of OsO4, diborane, NaBH4, LiAlH4 in organic synthesis. Photo Chemistry of ketones, photo oxygenation, photo reduction, photocycloaddition, Paterno – Buchi reaction, Di-pi-methane rearrangement. Cis-trans isomerisation, Barton reaction and photo-Fries reaction.
Elements of symmetry – optical and geometric isomerism E.Z and R.S notations – Conformational analysis simple cyclic and acyclic systems – Effects of conformation on reactivity in acyclic compounds and cyclohexanes. Relative stabilities of cis–trans isomers.
Unit – VIII: Natural Products and Drugs: Carbohydrates – Classification – configuration and general reactions of monosaccharides – Chemistry of glucose, fructose, sucrose and maltose, important compounds in Chemistry – Dyes – azo triphenylmethane and phthalein groups – indigo – alizarin vitamins, hormones, proteins – structural determination –Terpenoids – classification, isolation, general properties of citral, α –Terpineol, menthol, champhor.
Alkaloids and Flavonoids – Nomenclature and classification general properties – colour reactions, structure for Nicotine, atropine, cocaine, quinine, morphine and Heroin.
Drugs: Pharmacological actions, therapeutic uses and screening tests of the following drugs – opium alkaloids – morphine, heroin, antibiotics – synthetic analgesics – pethidine, methadone – barbiturates – tranquilizers – phenothiazines, meprobamate, diazepam – stimulants – amphetamines, imipramines – hallucinogens – cannabinoids, LSD – hypnosis and sedatives – antipyretics, analgesics, antiseptics and disinfectants – Alcohol – manufacture of ethyl alcohol and liquors – constituents of liquors – estimation of alcohol contents in liquors –denaturation, denaturants, industrial alcohol and power alcohol.
Unit – IX: Poisons and Pesticides: Definition of poisons – Mode of action of poisons – Extraction and purification of poisons in toxicological analysis – Volatile poisons – metallic poisons – non- volatile organic poisons – water-soluble compounds – protein precipitation methods. Estimation of the following poisons – Carbon monoxide, cyanide, formaldehyde, methanol, chloral, chloroform, phenols, cresols, phosphorus and amphetamines – Signs and symptoms of H2SO4, HNO3, CO2, H2 S poisoning. Analytical methods for the estimation of ethyl alcohol. Metallic poison –signs, symptoms of arsenic, mercury, lead and copper – Reinch test – Marsch Berzelius and Gutzeit tests – volumetric, colorimetric and instrumental methods of analysis of the above metals. Pesticides & Insecticides – Definition – general propertics poisonous nature – detection
& isolation.
Unit – X: Analytical Chemistry and Instrumental methods: Significant figures – precession & accuracy – Errors – minimizing methods – estimation of errors – rejection of observation.
Absorption, partition chromatography – Gas Chromatography – HPLC – Solvent extraction and ion exchange methods – atomic absorption spectroscopy – Electron analytical techniques voltammetry, cyclic voltammetry, polarogaphy, amperonmetry, Coulmetry and conductometry, ion-Selective electrodes – TGA, DTA and DSC.
TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer Paper II Syllabus:
Part A: கட்டாயத் தமிழ்மொழித் தகுதித் தேர்விற்கான பாடத்திட்டம் (கொள்குறிவினாவிற்கான தலைப்புகள்)
பத்தாம் வகுப்புத் தரம்
Part B: General Studies (Degree Standard)
(Topics for Objective Type)
1. General Science
2. Current Events
3. Geography
4. History and Culture of India
5. Indian Polity
6. Indian Economy
7. Indian National Movement
8. History, Culture, Heritage, and Socio-Political Movements of Tamil Nadu
9. Development Administration in Tamil Nadu
10. Aptitude & Mental Ability Tests
To see the complete TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer Chemistry Paper I & Paper II Syllabus PDF Download, check the link – TNPSC JSO Chemistry Syllabus PDF
To see other subjects TNPSC JSO Syllabus and Exam pattern 2023, check the link – TNPSC JSO Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2023