TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer Biology Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2023:
Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission (TNPSC) has given an employment notification for the recruitment of 31 Junior Scientific Officers in the Tamil Nadu Forensic Sciences Subordinate Service. Candidates with an M.Sc. Degree in a relevant stream looking for TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer check the Official notification @ www.tnpsc.gov.in or you can see it below. Eligible candidates can apply online directly and also see the TNPSC JSO Exam Pattern, Syllabus, Education Qualification, Selection Process, and Important details below. Check the complete TNPSC JSO Biology Syllabus available both in Tamil & English before preparing for Written Examination(CBT). See TTNPSC JSO Biology Syllabus 2023 and Exam Pattern below:
TNPSC JSO Paper I Syllabus for Biology – questions based on PG Degree Standard. TNPSC JSO Paper II Syllabus is based on Tamil Eligibility Test & General Studies. Check the complete JSO Biology Syllabus below both in text and in PDF format. Interested candidates check the complete syllabus and exam pattern of JSO below and also download the same. See the TNPSC JSO Biology Exam Pattern and Syllabus PDF Tamil and English below:
To see the complete Notification of TNPSC JSO Recruitment, check the link – TNPSC JSO Recruitment 2023
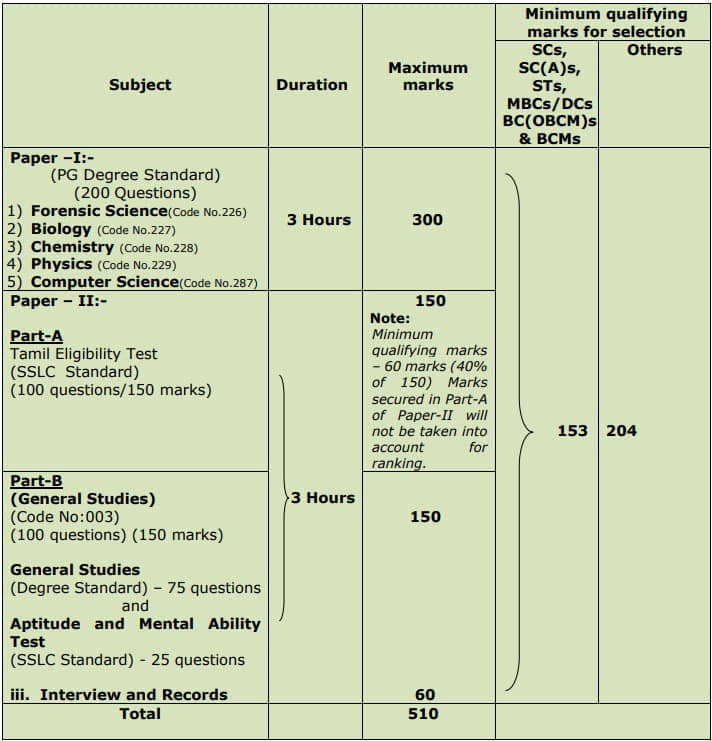
TNPSC JSO Biology Exam Pattern:
TNPSC JSO Biology Selection is based on a Written Examination (Objective Type) (Computer Based Examination)
– Written Examination is of Paper-I: Biology (PG Degree Standard) and Paper-II: Part A (Tamil Eligibility Test) & Part B (General Studies)
Junior Scientific Officer Paper I Biology Syllabus PDF:
The complete syllabus for JSO in Tamil and English is given below. See the full TNPSC JSO Paper I Syllabus below:
Paper I – Syllabus: Biology (PG Degree Standard)
Unit – I:
General classification and salient features of Invertebrata and vertebrata – Metamorphosis and regeneration in lower forms of animal – Economic importance of oyster, honey bee, Silkworm – Agricultural pests and their control – Larval forms of crustacean and Echinodermata – Classification and identification of poisonous and nonpoisonous snakes and types of snake venom. Evolution: Theories, types and factors influencing evolution Evidences of human evolution – Human genetics: Pedigree analysis, lod score for linkage testing, Karyotyping, Significance of human genome project.
Unit – II:
Structural organization and importance of animal cells – Muscle cells – Cardiac, Striated and non- striated muscle cells– Hepatocytes Neurons, Nephrons, Karatocytes, immune and endocrine cells. Functions of hormones and their receptors – Impact of sex hormones in human behavior.
Chronobiology: the importance of circadian rhythm and human biological clock – DNA analysis inpaternity testing – Cell counting of WBC and RBC.Functions and disorders of Digestive, Respiratory, Cardiovascular Nervous, Muscular, Excretory, Reproductive, and Integumentary systems.
Developmental biology: production of sperm and egg, Fertilization – Zygote, Cleavage. Blastulation, gastrulation, and formation of germ layers in animals and organogenesis –determination of sex by Amniocentosis.
Entomology: Insect classification – Beneficial and harmful insects – Role of insects in the decomposition of decayed materials – Exploiting insect olfaction in forensic studies – Importance of ants, blowflies, and beetles in forensic investigation.
Unit – III:
Fundamentals of Anthropology
Meaning – Scope and branches of Anthropology – Basic concepts/ principles of Physical or Biological Anthropology – Anthropology and its relation with other Social, Biological, and Medical Sciences – Analysis of kinship – Health and Ethno medicine – Population dynamics with special reference to Tamil Nadu – Applied and developmental
Anthropology – Tribal, Rural, and Urban Communities
Research Methodology- Anthropological research – Fieldwork Tradition, Methods and Techniques, Qualitative and Quantitative research Methods, Observation, Case study, Ethnography, Life histories and Personal documents, Visual Anthropology, Genealogical Methods.
Unit – IV:
Physical / Biological Anthropology
Position of human being in the animal kingdom – Human Evolution – Theories of human evaluation, Human growth, and development – Factors affecting for growth, Demographic growth variation, Sex and Gender – Bio-cultural dimensions, Race and Ethnicity – Major racial groups of India, Ethnicity and contemporary relevance – Applied physical anthropology – Anthropometry and its uses, DNA Technology, genetic diseases, Forensic Anthropology and criminal investigations.
Unit -V:
Chemistry of Biomolecules
Carbohydrates – Structure and functions [Mono, Di &Polysaccharides] – Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism and its laboratory diagnosis.
Proteins and Amino acids – Types, structure and Function.
Lipids – Types structure and functions. Sterols –Cholesterol.Disorders of lipid metabolism and its laboratory diagnosis.
Nucleic acid – DNA – Types, structure and functions RNA – Types, structure and functions
Enzymes – Classification and properties of enzymes, Coenzymes, Marker enzymes
Hormones- Classes and functions of hormones
Unit -VI:
Biochemical and Molecular Techniques
Blood and its composition – WBC, RBC, and Platelets. Blood clotting, Blood grouping, Crossmatching and
compatibility tests, Blood smear analysis, HLA typing.
Antigens and Immunoglobins – Classes and functions. Collection and Preservation of Biological fluids [Blood, Urine, CSF, Amniotic fluid, Semen, Sputum and Saliva].Normal and Abnormal constituents of Biological fluids.
Isolation of DNA from blood samples, Agarose gel Electrophoresis, PCR, DNA Sequencing, RAPD, RFLP, DNA
Fingerprinting -STR Typing.
Isolation of Proteins from a blood sample, SDS PAGE, RIA, ELISA, FISH. Ames test, Comet Assay.
Unit – VII:
Origin of Microbiology, Contribution of Louis Pasteur, Alexander Flemming, Waksman, Robert Koch.Microscopy; Brightfield, Phase contrast, Fluorescent, Electron Microscopy and Confocal Microscopy. Staining techniques.
Cultivation of Microorganisms, Preparation of culture media, Sterilization techniques, Preservation techniques, Identification of Microorganisms; Conventional and Molecular techniques.
Host-parasite interaction, Microbial diseases, Nosocomial infection, Zoonotic diseases, Foodborne diseases,
Microbial diseases of medical negligence. Bioterrorism and Biohazards.
Unit – VIII:
DNA profiling, Genetic code, Mutation and DNA polymorphism, Microbial nanotechnology, Infectomics.
Biodeterioration of fibres and leather, Bioremediation, Bioconversion – Biogas technology, Environmental microbiology – Microbiology of air, water, and soil. Role of microbes in the production of fermentation products.
Production of antibiotics, Enzymes, Pigments, Insulin, Interferon, Monoclonal antibodies and Growth Hormones. Recombinants DNA technology.
Microbial biofertilizers, Microbial biopesticides, and Microbial degradation of synthetic pesticides.
Unit – IX:
Plant Diversity, Cell Biology – Taxonomy and Paleo botany, Plant PhysiologyPlant biochemistry, Plant pathology
Plant Diversity – Algae, Fungi, Bryophyte, pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, lichen.
Cell Biology – Cell structure and functions
Taxonomy– Principals of Taxonomy and phylogeny of angiosperms, Nomenclature of plants, Monocotyledons and dicotyledons
Paleo botany – Fossil plants
Plant Physiology and Plant biochemistry – Enzymes, Protein, Aminoacid and photosynthesis, respiration
Plant pathology – Bacterial, Fungal, and Viral Diseases of Plants.
Unit- X:
Plant Anatomy, Embryology, Genetics, Economic Botany, Ethnobotany, Environmental Botany Plant Anatomy – Cell cycle, Cell division, Tissue system and secondary growth, Fruit wall, and seed coat.
Embryology – Embryogenesis, Polyembryony, Double fertilization, Somatic Embryogenesis and Pollen grains.
Genetics – Mendelism, Linkage, crossing-over, chromosome mapping, RAPD and RFLP Techniques.
Economic Botany – Wood and Wood Products, Fatty Oils, and Vegetable Oils. Tannins and Dyes.
Ethnobotany – Ethno Medicinal Plants, Narcotic Plants.
Environmental Botany – Plant adaptations, Hydrophytes, Xerophytes, Mesophytes, Epiphytes, Halophytes, and Mangrove vegetation. Ecological Indicators, Forest and Forest Management.
TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer Paper II Syllabus:
Part A: கட்டாயத் தமிழ்மொழித் தகுதித் தேர்விற்கான பாடத்திட்டம் (கொள்குறிவினாவிற்கான தலைப்புகள்)
பத்தாம் வகுப்புத் தரம்
Part B: General Studies (Degree Standard)
(Topics for Objective Type)
1. General Science
2. Current Events
3. Geography
4. History and Culture of India
5. Indian Polity
6. Indian Economy
7. Indian National Movement
8. History, Culture, Heritage, and Socio-Political Movements of Tamil Nadu
9. Development Administration in Tamil Nadu
10. Aptitude & Mental Ability Tests
To see the complete TNPSC Junior Scientific Officer Biology Paper I & Paper II Syllabus PDF Download, check the link – TNPSC JSO Biology Syllabus PDF
To see other subjects TNPSC JSO Syllabus and Exam pattern 2023, check the link – TNPSC JSO Syllabus and Exam Pattern 2023