TNPSC Indian Economy – Planning Commission and Niti Ayog:
Indian Economics questions are more important for the TNPSC Group 2 Prelims Exam. You will get 6 t0 8 marks from that Indian Economy portion. On this page, TNPSC Group 2, 2a, and Group 4 TNPSC Indian Economy Study Materials questions with answers are uploaded. Go through TNPSC Indian Economy Notes, Questions, and Answers below for the prelims exam.
Students who are preparing for the Group exam concentrate more on the maths part. you will easily score more marks in the Economics part. For students’ benefit, we upload TNPSC Indian Economy English and Tamil questions and answers in PDF for download. TNPSC aspirants can download and use it for the group prelims exam. kindly download TNPSC Indian Economy PDF given below:
Meaning of Development and Underdevelopment:
The concept “development” refers to the structural changes towards betterment. Until the World War II, interest was rarely shown on the problems of the present-day third World Countries. After the Second World War, economists started devoting their attention towards analyzing the problems of underdeveloped countries and formulating theories and models of development and growth.
The Under Developed Countries (UDCs) were once the colonies of England and other European countries. After becoming free and independent, there was an awakening to march towards economic development.
Approaches to Economic Development:
There are two main approaches to the concept of development viz i) the traditional approach and ii) the new welfare-oriented approach.
1. Traditional Approach:
- The traditional approach defines development strictly in economic terms.
- The increase in GNP is accompanied by a decline in share of agriculture in output and employment while those of manufacturing and service sectors increase. It emphasizes the importance of industrialization.
- It was assumed that growth in GNP per capita would trickle down to people at the bottom.
2. New Welfare oriented Approach:
- During the 1970s, economic development was redefined in terms of reduction of poverty, ‘inequality’ and unemployment within the context of a growing economy.
- In this phase, ‘Redistribution with Growth’ became the popular slogan.
- To quote Michael P. Todaro, “Development must, therefore, be conceived as a multidimensional process involving major changes in social structures, popular attitudes, and national institutions as well as the acceleration of growth, the reduction of inequality and the eradication of absolute poverty”.
Underdevelopment:
- The UDCs are characterized by a predominance of primary sector i.e. agriculture, low per capita income, widespread poverty, wide inequality in the distribution of income and wealth, overpopulation, low rate of capital formation, high rate of unemployment, technological backwardness, dualism, etc.
Features of an Underdeveloped Economy:
- The term ‘underdeveloped country’ is relative.
- The World Bank in its World Development Report classified various countries on the basis of Gross National Income (GNI) Per Capita.

Meaning of Underdevelopment
- The term underdevelopment refers to that state of an economy where levels of living of masses are extremely low due to very low levels of Percapita income, resulting from low levels of productivity and high growth rate of population.
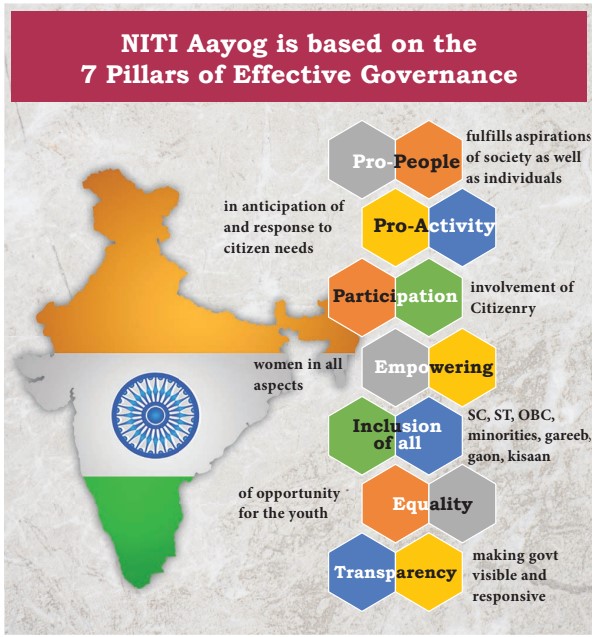
NITI Aayog:
- The NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) was formed on January 1, 2015, through a Union Cabinet resolution. NITI Aayog is a policy think-tank of the Government of India. It replaced the Planning Commission from 13th August 2014. The Prime Minister is the Chairperson of NITI Aayog and Union Ministers will be Ex-officio members.
- The Vice-Chairman of the NITI Aayog is the functional head and the first Vice-Chairman was Arvind Panangariya.
Functions of NITI Aayog:
1. Cooperative and Competitive Federalism:
- To enable the States to have active participation in the formulation of national policy.
2. Shared National Agenda:
- To evolve a shared vision of national development priorities and strategies with the active involvement of States.
3. Decentralized Planning:
- To restructure the planning process into a bottom-up model.
4. Vision and Scenario Planning:
- To design medium and long-term strategic frameworks towards India’s future.
5. Network of Expertise:
- To mainstream external ideas and expertise into government policies and programmes through a collective participation.
6. Harmonization:
- To facilitate harmonization of actions across different layers of government, especially when involving cross-cutting and overlapping
issues across multiple sectors; through communication, coordination, collaboration and convergence amongst all the stakeholders.
7. Conflict Resolution:
- To provide platform for mutual consensus to inter-sectoral, inter-departmental, inter-state as well as centre-state issues for all speedy execution of the government programmes.
8. Coordinating Interface with the World:
- It will act nodal point to harness global expertise and resources coming from International organizations for India’s developmental process.
9. Internal Consultancy:
- It provides internal consultancy to Central and State governments on policy and programmes.
10. Capacity Building:
- It enables to provide capacity building and technology up-gradation across government, benchmarking with latest global trends, and providing managerial and technical know-how.
11. Monitoring and Evaluation:
- It will monitor the implementation of policies and progammes and evaluate the impacts.
- NITI Aayog is also bringing about a greater level of accountability. It has established a development monitoring and evaluation office which collects data on the performance of various ministries.
- Using such data, the Aayog makes performance-based ranking of states to foster a spirit of competitive federalism. The success of NITI Aayog can be evaluated after a substantial period of time
