10th Maths Book Back Question and Answers – Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2:
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Standard Maths Book Back Questions with Answers PDF uploaded and the same given below. Class-tenth candidates and those preparing for TNPSC exams can check the Maths Book Back Answers PDF below. Samacheer Kalvi Class 10th Std Maths Book Back Answers Chapter 2 Exercise 2.2 Solutions are available below. Check the complete Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths – Numbers and Sequences Ex 2.2 Book Back Answers below:
We also provide class 10th other units Maths Book Back One and Two Mark Solutions Guide on our site. Students looking for the 10th standard Maths Ex 2.2 – Numbers and Sequences Book Back Questions with Answer PDF
For the complete Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Back Solutions Guide PDF, check the link – Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Back Answers
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Back Answers – Ex 2.2 Numbers and Sequences
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book Subject One Mark, Two Mark, Five Mark Guide questions and answers are below. Check Maths Book Back Questions with Answers. Take the printout and use it for exam purposes.
For Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Book PDF, check the link – 10th Maths Book PDF
Chapter 2
Ex 2.2 Numbers and Sequences
- For what values of the natural number n, 4n can end with the digit 6?
Solution:
4n = (2 × 2)n = 2n × 2n
2 is a factor of 4n.
So, 4n is always even and end with 4 and 6.
When n is an even number say 2, 4, 6, 8 then 4n can end with the digit 6.
Example:
42 = 16
43 = 64
44 = 256
45 = 1,024
46 = 4,096
47 = 16,384
48 = 65, 536
49 = 262,144
2.If m, n are natural numbers, for what values of m, does 2n × 5m ends in 5?
Answer:
2n is always even for any values of n.
[Example. 22 = 4, 23 = 8, 24 = 16 etc]
5m is always odd and it ends with 5.
[Example. 52 = 25, 53 = 125, 54 = 625 etc]
But 2n × 5m is always even and end in 0.
[Example. 23 × 53 = 8 × 125 = 1000
22 × 52 = 4 × 25 = 100]
∴ 2n × 5m cannot end with the digit 5 for any values of m.
3. Find the H.C.F. of 252525 and 363636.
Solution:
To find the H.C.F. of 252525 and 363636
Using Euclid’s Division algorithm
363636 = 252525 × 1 + 111111
The remainder 111111 ≠ 0.
∴ Again by division algorithm
252525 = 111111 × 2 + 30303
The remainder 30303 ≠ 0.
∴ Again by division algorithm.
111111 = 30303 × 3 + 20202
The remainder 20202 ≠ 0.
∴ Again by division algorithm
30303 = 20202 × 1 + 10101
The remainder 10101 ≠ 0.
∴ Again using division algorithm
20202 = 10101 × 2 + 0
The remainder is 0.
∴ 10101 is the H.C.F. of 363636 and 252525.
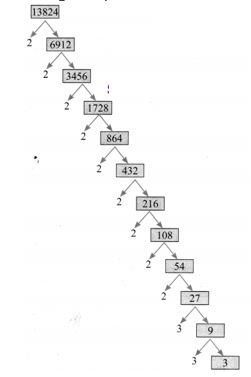
4.If 13824 = 2a × 3b then find a and b.
Solution:
If 13824 = 2a × 3b
Using the prime factorisation tree
13824 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 29 × 33 = 2a × 3b
∴ a = 9, b = 3.
5.If p1x1 × p2x2 × p3x3 × p4x4 = 113400 where p1, p2, p3, p4 are primes in ascending order and x1, x2, x3, x4 are integers, find the value of P1, P2, P3, P4 and x1, x2, x3, x4.
Solution:
If p1x1 × p2x2 × p3x3 × p4x4 = 113400
p1, p2, p3, P4 are primes in ascending order, x1, x2, x3, x4 are integers.
using Prime factorisation tree.

113400 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 5 × 7
= 23 × 34 × 52 × 7
= p1x1 × p2x2 × p3x3 × p4x4
∴ p1= 2, p2 = 3, p3 = 5, p4 = 7, x1 = 3, x2 = 4, x3 = 2, x4 = 1.
6.Find the L.C.M. and H.C.F. of 408 and 170 by applying the fundamental theorem of arithmetic.
Solution:
408 and 170.
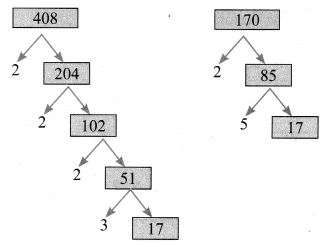
408 = 23 × 31 × 171
170 = 21 × 51 × 171
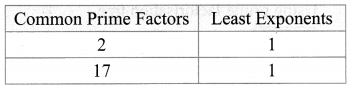
∴ H.C.F. = 21 × 171 = 34.
To find L.C.M, we list all prime factors of 408 and 170, and their greatest exponents as follows.
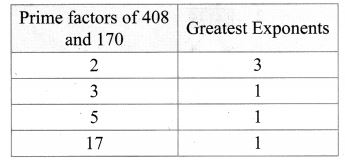
∴ L.C.M. = 23 × 31 × 51 × 171
= 2040.
7.Find the greatest number consisting of 6 digits which is exactly divisible by 24, 15, 36?
Solution:
To find L.C.M of 24, 15, 36
24 = 23 × 3
15 = 3 × 5
36 = 22 × 32
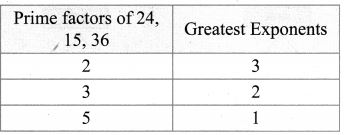
∴ L.C.M = 23 × 32 × 51
= 8 × 9 × 5
= 360
If a number has to be exactly divisible by 24, 15, and 36, then it has to be divisible by 360. The greatest 6 digit number is 999999.
Common multiplies of 24, 15, 36 with 6 digits are 103680, 116640, 115520, …933120, 999720 with six digits.
∴ The greatest number consisting 6 digits which is exactly divisible by 24, 15, 36 is 999720.
8. What is the smallest number that when divided by three numbers such as 35, 56 and 91 leaves the remainder 7 in each case?
Answer:
Find the L.C.M of 35, 56, and 91
35 – 5 × 7 56
56 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 7
91 = 7 × 13
L.C.M = 23 × 5 × 7 × 13
= 3640
Since it leaves the remainder 7
The required number = 3640 + 7
= 3647
The smallest number is = 3647
9. Find the least number that is divisible by the first ten natural numbers.
Solution:
The least number that is divisible by the first ten natural numbers is 2520.
Hint:
1,2, 3,4, 5, 6, 7, 8,9,10
The least multiple of 2 & 4 is 8
The least multiple of 3 is 9
The least multiple of 7 is 7
The least multiple of 5 is 5
∴ 5 × 7 × 9 × 8 = 2520.
L.C.M is 8 × 9 × 7 × 5
= 40 × 63
= 2520
Other Important Links for 10th Maths Book Back Answers Solutions:
For 10th Maths Book chapter 2 book back question and answers, check the link – Samacheer kalvi 10th Maths Chapter 2 Numbers and Sequences
Click here for the complete Samacheer Kalvi 10th Book Back Solution Guide PDF – 10th Maths Book Back Answers