8th Science Unit 18 – Organisation of life Book Back Answers:
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Standard New Science Book Back 1 Mark and 2 Mark Question & Answers PDF uploaded and available below. Class 8 New Syllabus 2021 to 2022 Book Back Question & Answer available for both English and Tamil Mediums. Class 8th Science Book Unit 18 – Organisation of Life Answers/Solutions are provided on this page. 8th Std Science Book consists of 23 units, All Science Book Back One, and Two Mark Solutions are given below. Check the Organisation of life – 8th standard samacheer kalvi Unit 18 Answers here.
Check Unit wise and Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Back Solutions Answers PDF format for Free Download. English, Tamil, Maths, Science, and Social Science Book Back Question and Answer is available in PDF. Class 8th Standard Science Book Back Answers PDF. Check the Science book back Answers below. See below for the 8th New Science Syllabus Book Back guide/Answers free PDF download. Organisation of life 8th standard samacheer kalvi questions and answers are given below.
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Back Solutions PDF:
8th Science Subject 1 Mark and 2 Mark Solutions PDFs are available below. Click the Download option to download the book back 1 Mark & 2 Mark questions and answers. Take the printout and use it for exam purposes. Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Unit 18 Answers are given below.
Science Book Back Answers
Unit 18 – Organisation of Life
I. Choose the correct answers
1. ……………… is tough and thick white sheath that protect the inner parts of the eye.
(a) Sclera
(b) Conjunctiva
(c) Cornea
(d) Iris
Answer:
(a) Sclera
2. Maintenance of constant internal environment of the body is known as ………………
(a) Homeostasis
(b) Homeophytes
(c) Homeokinesis
(d) Homeophilics
Answer:
(a) Homeostasis
3. In the absence of oxygen, glucose is broken down into ………………
(a) Lactic acid
(b) Citric acid
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Nitric acid
Answer:
(a) Lactic acid
4. ……………… cells are specialised cells that can be transformed into any kind of cells.
(a) Nerve
(b) Stem
(c) Heart
(d) Bone
Answer:
(b) Stem
5. The process of air passing in and out the lungs is called ………………
(a) Inhalation
(b) Exhalation
(c) Breathing
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Breathing
6. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a ………………
(a) Higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
(b) Lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
7. The erythrocyte is placed in ……………… solution which has lesser concentration of solutes and greater concentration of water than in the cytoplasm.
(a) Hypotonic
(b) Hypertonic
(c) Neutral
(d) Acidic
Answer:
(a) Hypotonic
II. Fill in the blanks
- ……………… is the structural and functional unit of living organisms.
- The largest cell is egg of an ………………
- ……………… is a good example for anaerobic respiration.
- ……………… nerve is located at the end of the eyes behind the retina.
- The size of the cells are measured in units of ………………
Answer:
- Cell
- Ostrich
- Fermentation
- Optic
- Microns
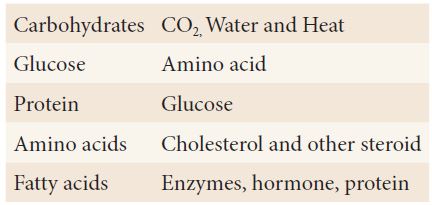
III. Match the following:
Answer:
1 – 3; 2 – 1; 3 – 2; 4 – 5; 5 – 4
IV. Write true or False. If false, give the correct answer
1. In hypotonic condition, concentration of the external and the internal solution of the organism are same.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
The concentration of external solution is less compared to concentration of internal solution of the organism.
2. Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of lower concentration to higher concentration.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement:
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration.
3. Human beings are warm blooded in nature.
Answer:
True.
4. The larynx has fold of tissue which vibrate with the passage of air to produce.
Answer:
True.
5. Aqueous humour plays an important role in maintaining the shape of the eye.
Answer:
True.
V. Answer in brief
1. What is cell differentiation?
Answer:
Our body develops from a single cell called zygote. The zygote undergoes mitotic division to form many cells of different shape, size and content. These cells attain change in structure and function which is called differentiation. This form the foetus.
2. State different types of tissues.
Answer:
Depending on the basis of their structure and function, tissues can be classified into four types.
- Epithelial (covering) tissue for protection.
- Muscular (contractile) tissue for movements and locomotion.
- Connective (supporting) tissue for binding different structures of body.
- Nervous tissue for conduction of nerve impulses.
3. Mention the function of ‘Alveoli’?
Answer:
- Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs.
- They are the workhouses of the respiratory system.
- The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide take place in alveoli of the lungs.
4. Name the processes by which air enters and comes out of our lungs?
Answer:
- The process of taxing air into the lungs is called inspiration or inhalation.
- The process of expelling air from the lungs is called expiration or exhalation.
5. Differentiate between Osmoconformers and Osmoregulators?
Answer:
There are two major types of Osmoregulation:
Osmoconformers:
These organisms try to maintain the osmolality of their body matching with their surroundings. Most of the invertebrates, marine organisms are osmoconformers.
Osmoregulators:
These organisms maintain their internal osmolality, which can be extremely different from that of the surrounding environment, through physiological processes.
6. Define Metabolism?
Answer:
- Metabolism is the sum of chemical reactions by which living organisms sustain their life.
- Metabolism consists of anabolism (the buildup of substances) and catabolism (the breakdown of substances).
Other Important links for 8th Science Book Back Answers:
Click here for Samacheer Kalvi 8th Science Book Back Solutions – 8th Science Book Back Answers