TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Exam Pattern, Syllabus, and Notification 2023:
The Southern Power Distribution Company of Telangana Limited (TSSPDCL) has given an employment notification for recruiting Assistant Engineer on a regular basis. Candidates with Bachelor’s Degree in Engineering can check the job vacancies at https://www.tssouthernpower.com/ or see below. Interested candidates go through the official website and apply till 15-03-2022. Also see TSSPDCL Asst Engineer Notification 2023, Important Dates, Selection Procedure, Exam Pattern, and complete syllabus PDF is given below for free download below. Check the TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer Syllabus 2023 below:
List of TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer Recruitment 2023 Details:
Below is The Southern Power Distribution Company of Telangana Limited recruitment details:
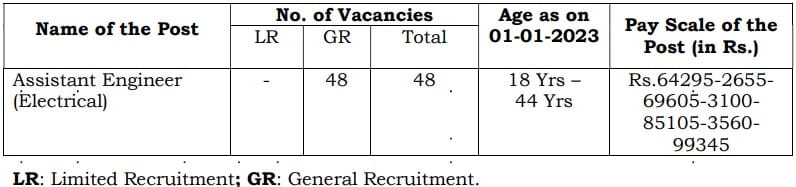
Vacancy Details:
- Post Name: Assistant Engineer (Electrical)
- No. of Vacancies: 48
Job Location: Telangana.
Important Dates for TSSPDCL Asst Engineer Jobs 2023:
- Starting date for Submission of Online Application and Fee payment: 23-02-2023
- Last date for Submission of the Online Application and Fee payment: is 15-03-2023
- Application Edit facility (for making corrections, if any): From 18.03.2023 To 21.03.2023
- Downloading of Hall tickets from 24-04-2023
- Date of written examination: 30-04-2023
For complete TSSPDCL Asst Engineer Official Notification 2023 details, Check the link – TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer Recruitment 2023
TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer Exam Pattern:
The Southern Power Distribution Company of Telangana Limited Asst Engineer posts selection based on Written Examination.
| Written Exam Pattern | No. of Questions | No. of Marks |
| Section A | 80 questions | 80 marks |
| Section B | 20 questions | 20 marks |
| Total | 100 questions | 100 marks |
| The duration of the written examination will be 2 hrs. (120 minutes). | ||
TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer Syllabus 2023:
Below is the complete syllabus of TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer recruitment 2023 and the same syllabus available in PDF for free download
For the complete TSSPDCL Asst Engineer Syllabus 2023 PDF, check the link – TSSPDCL Assistant Engineer Syllabus PDF
Section-A: 80 Marks.
I. Engineering Mathematics
Linear Algebra: Matrix Algebra, Systems of linear equations, Eigenvalues, Eigenvectors.
Calculus: Mean value theorems, Theorems of integral calculus, Evaluation of definite and improper integrals, Partial Derivatives, Maxima and minima, Multiple integrals, Fourier series, Vector identities, Directional derivatives, Line integral, Surface integral, Volume integral, Stokes’s theorem, Gauss’s theorem, Green’s theorem.
Differential equations: First-order equations (linear and nonlinear), Higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients, Method of variation of parameters, Cauchy’s equation, Euler’s equation, Initial and boundary value problems, Partial Differential Equations, Method of separation of variables.
Complex variables: Analytic functions, Cauchy’s integral theorem, Cauchy’s integral formula, Taylor series, Laurent series, Residue theorem, Solution integrals.
Probability and Statistics: Sampling theorems, Conditional probability, Mean, Median, Mode, Standard Deviation, Random variables, Discrete and Continuous distributions, Poisson distribution, Normal distribution, Binomial distribution, Correlation analysis, and Regression analysis.
Numerical Methods: Solutions of nonlinear algebraic equations, Single and Multi‐step methods for differential equations.
Transform Theory: Fourier Transform, Laplace Transform, z‐Transform.
II. Electrical Engineering
Electric Circuits
Network graph, KCL, KVL, Node and Mesh analysis, Transient response of dc and ac networks, Sinusoidal steady‐state analysis, Resonance, Passive filters, Ideal current and voltage sources, Thevenin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, Superposition theorem, Maximum power transfer theorem, Two‐port networks, Three phase circuits, Power and power factor in ac circuits.
Electromagnetic Fields
Coulomb’s Law, Electric Field Intensity, Electric Flux Density, Gauss’s Law, Divergence, Electric field and potential due to point, line, plane, and spherical charge distributions, Effect of the dielectric medium, Capacitance of simple configurations, Biot‐Savart’s law, Ampere’s law, Curl, Faraday’s law, Lorentz force, Inductance, Magnetomotive force, Reluctance, Magnetic circuits, Self, and Mutual inductance of simple configurations.
Signals and Systems
Representation of continuous and discrete‐time signals, Shifting and scaling operations, Linear Time Invariant and Causal systems, Fourier series representation of continuous periodic signals, Sampling theorem, Applications of Fourier Transform, Laplace Transform, and z-Transform.
Electrical Machines
Single phase transformer: equivalent circuit, phasor diagram, open circuit, and short circuit tests, regulation, and efficiency; Three phase transformers: connections, parallel operation; Auto‐transformer, Electromechanical energy conversion principles, DC machines: separately excited, series and shunt, motoring and generating mode of operation and their characteristics, starting and speed control of dc motors; Three phase induction motors: the principle of operation, types, performance, torque-speed characteristics, no-load and blocked rotor tests, equivalent circuit, starting and speed control; Operating principle of single phase induction motors; Synchronous machines: cylindrical and salient pole machines, performance, regulation and parallel operation of generators, starting of synchronous motor, characteristics; Types of losses and efficiency calculations of electric machines.
Power Systems
Power generation concepts, ac and dc transmission concepts, Models and performance of transmission lines and cables, Series and shunt compensation, Electric field distribution and insulators, Distribution systems, Per‐unit quantities, Bus admittance matrix, Gauss-Seidel and Newton-Raphson load flow methods, Voltage and Frequency control, Power factor correction, Symmetrical components, Symmetrical and unsymmetrical fault analysis, Principles of over‐current, differential and distance protection; Circuit breakers, System stability concepts, Equal area criterion.
Control Systems
Mathematical modeling and representation of systems, Feedback principle, transfer function, Block diagrams and Signal flow graphs, Transient and Steady‐state analysis of linear time-invariant systems, Routh-Hurwitz and Nyquist criteria, Bode plots, Root loci, Stability analysis, Lag, Lead and Lead‐Lag compensators; P, PI, and PID controllers; State space model, State transition matrix.
Electrical and Electronic Measurements
Bridges and Potentiometers, Measurement of voltage, current, power, energy, and power factor; Instrument transformers, Digital voltmeters, and multimeters, Phase, Time, and Frequency measurement; Oscilloscopes, Error analysis.
Analog and Digital Electronics
Characteristics of diodes, BJT, MOSFET; Simple diode circuits: clipping, clamping, rectifiers; Amplifiers: Biasing, Equivalent circuit and Frequency response; Oscillators and Feedback amplifiers; Operational amplifiers: Characteristics and applications; Simple active filters, VCOs and Timers, Combinational and Sequential logic circuits, Multiplexer, Demultiplexer, Schmitt trigger, Sample and hold circuits, A/D and D/A converters, 8085 Microprocessor: Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing.
Power Electronics
Characteristics of semiconductor power devices: Diode, Thyristor, Triac, GTO, MOSFET, IGBT; DC to DC conversion: Buck, Boost, and Buck-Boost converters; Single and three phase configuration of uncontrolled rectifiers, Line commutated thyristor-based converters, Bidirectional ac to dc voltage source converters, Issues of line current harmonics, Power factor, Distortion factor of ac to dc converters, Single phase and three phase inverters, Sinusoidal pulse width modulation.
Section-B: 20 Marks.
General Awareness and Numerical Ability :
i) Analytical & Numerical Ability
ii) General Awareness
iii) English
iv) Related to Telangana Culture & Movement and v) Computer Knowledge